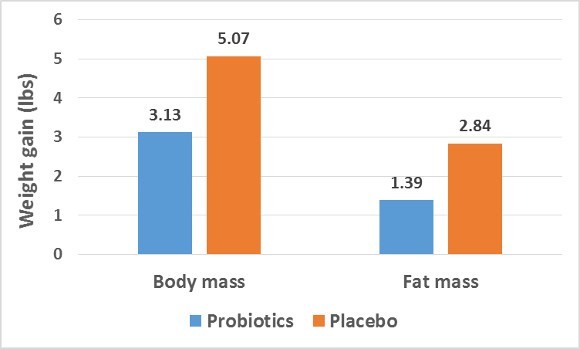
Probiotics are live microorganisms that have health benefits when consumed (1).

These are usually beneficial bacteria that serve some function in the body.
Probiotics have all sorts of powerful benefits for your body and brain.
They may improve digestive health, reduce depression and promote heart health (2, 3, 4).
Some evidence even suggests that they may give you better looking skin (5).
Getting probiotics from supplements is popular, but you can also get them from foods that are prepared by bacterial fermentation (fermented foods).
Here is a list of 11 super healthy fermented foods that contain live probiotics.
1. Yogurt
Yogurt is a highly nutritious dairy product made from fermented milk.
The milk is fermented with friendly bacteria, mainly lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria (6).
Eating yogurt has been associated with many health benefits, including improved bone health. It is also beneficial for people with high blood pressure (7, 8).
In children, yogurt may help reduce diarrhea caused by antibiotics. It can even help relieve the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (9, 10, 11).
Additionally, yogurt may be better than milk for people with lactose intolerance. This is because the bacteria turn some of the lactose into lactic acid, which is also why yogurt tastes sour.
However, keep in mind that not all yogurt contains live probiotics. In some cases, the live bacteria have been killed during processing.
For this reason, make sure to choose yogurt with active or life cultures.
Also, make sure to always read the label on yogurt before you buy it. Even if it is labeled low-fat or fat-free, it may still be loaded with high amounts of added sugar.
Bottom Line: Probiotic yogurt is linked to a number of health benefits. It may also be more suitable than milk for people with lactose intolerance. Make sure to choose yogurt that has active or life cultures.
2. Kefir
Kefir is a fermented milk drink. It is made by adding kefir grains to cow or goat milk.

Kefir grains are not cereal grains, but rather cultures of lactic acid bacteria and yeast that look a bit like cauliflower.
The word kefir allegedly comes from the Turkish word keyfir, which means feeling good after eating (12).
In fact, kefir has been linked to various health benefits.
It may improve bone health, help with some digestive problems and protect against infections (2, 13, 14).
While yogurt is probably the best known probiotic food in the Western diet, kefir is actually a better source. Kefir contains several major strains of friendly bacteria and yeast, making it a diverse and potent probiotic (15).
Like yogurt, kefir is generally well-tolerated by people who are lactose intolerant (16).
Bottom Line: Kefir is a fermented milk drink. It is a better source of probiotics than yogurt, and people with lactose intolerance can often eat kefir with no problems.
3. Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut is finely shredded cabbage that has been fermented by lactic acid bacteria.

It is one of the oldest traditional foods and is popular in many countries, especially in Europe.
Sauerkraut is often used on top of sausages or as a side dish. It has a sour, salty taste and can be stored for months in an airtight container.
In addition to its probiotic qualities, sauerkraut is rich in fiber, as well as vitamins C, B and K. It is also high in sodium and contains iron and manganese (17).
Sauerkraut also contains the antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin, which are important for eye health (17, 18).
However, make sure to choose unpasteurized sauerkraut. Pasteurization kills the live and active bacteria.
Bottom Line: Sauerkraut is finely cut, fermented cabbage. It is rich in vitamins, minerals and antioxidants. Make sure to choose unpasteurized brands that contain live bacteria.
4. Tempeh
Tempeh is a fermented soybean product. It forms a firm patty, and people have described the flavor as nutty, earthy or similar to a mushroom.
Tempeh is originally from Indonesia but has become popular all over the world as an high-protein meat substitute.
The fermentation process actually has some surprising effects on its nutritional profile.
Soybeans are typically high in phytic acid, a plant compound that impairs the absorption of minerals like iron and zinc.
However, the fermentation process lowers the amount of phytic acid, which may increase the number of minerals the body is able to absorb from tempeh (19, 20).
Another interesting byproduct of this process is that the bacteria produce some vitamin B12, a nutrient that soybeans do not contain (21, 22, 23).
Vitamin B12 is mainly found in animal foods, such as meat, fish, dairy products and eggs (24).
This makes tempeh an overall great choice for vegetarians, as well as anyone looking to add a nutritious probiotic to their diet.
Bottom Line: Tempeh is a fermented soybean product. It is a popular, high-protein substitute for meat. It also contains a decent amount of vitamin B12, a nutrient found mainly in animal products.
5. Kimchi
Kimchi is a fermented, spicy Korean side dish.

Cabbage is usually the main ingredient, but it can also be made from other vegetables.
A mix of seasonings is used for flavors, such as red chili pepper flakes, garlic, ginger, scallion, and salt.
Kimchi contains the lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillus kimchi, as well as other lactic acid bacteria that may benefit digestive health (25, 26).
Kimchi made from cabbage is high in some vitamins and minerals, including vitamin K, riboflavin (vitamin B2) and iron (17).
Bottom Line: Kimchi is a spicy Korean side dish, usually made from fermented cabbage. It contains lactic acid bacteria, which may benefit digestive health.
6. Miso
Miso is a Japanese seasoning.

It is traditionally made by fermenting soybeans with salt and a type of fungus called koji.
Miso can also be made by mixing soybeans with other ingredients, like barley, rice, and rye.
This paste is most often used in miso soup, a popular breakfast food in Japan. Miso is typically salty, and you can buy it in many varieties, such as white, yellow, red and brown.
Miso is a good source of protein and fiber. It is also high in various vitamins, minerals and phytonutrients, including vitamin K, manganese, and copper (17).
Miso has also been linked to some health benefits.
One study reported that frequent miso soup consumption was associated with a lower risk of breast cancer in middle-aged Japanese women (27).
Another study found that women who ate a lot of miso soup had a reduced risk of stroke (28).
Bottom Line: Miso is a fermented soybean paste and a popular Japanese seasoning. It is rich in several important nutrients and may reduce the risk of cancer and stroke, especially in women.
7. Kombucha
Kombucha is a fermented black or green tea drink.

This popular tea is fermented by a friendly colony of bacteria and yeast. It is consumed in many parts of the world, especially Asia.
On the internet, there are many claims about the potential health effects of kombucha tea.
However, high-quality evidence on kombucha is lacking.
The studies that exist are the animal and test tube studies, and the results may not apply to humans (29).
Yet, because kombucha is fermented with bacteria and yeast, it does probably have health benefits related to its probiotic properties.
Bottom Line: Kombucha is a fermented tea drink. It is claimed to have a wide range of health benefits, but human evidence for these claims is currently lacking.
8. Pickles
Pickles (also known as gherkins) are cucumbers that have been pickled in a solution of salt and water.

They are left to ferment for some time, using their own naturally present lactic acid bacteria. This process is what makes them sour.
Pickled cucumbers are a great source of healthy probiotic bacteria, which may improve digestive health.
They are low in calories and a good source of vitamin K, an essential nutrient for blood clotting. Pickles also tend to be high in sodium (17).
It is important to note that pickles made with vinegar do not contain live probiotics.
Bottom Line: Pickles are cucumbers that have been pickled in salt water and fermented. They are low in calories and high in vitamin K. However, pickles made using vinegar do not have probiotic effects.
9. Traditional Buttermilk
The term buttermilk actually refers to a range of fermented dairy drinks.

However, there are two main types of buttermilk: traditional and cultured.
Traditional buttermilk is simply the leftover liquid from making butter. Only this version contains probiotics, and it is sometimes called Grandmas probiotic.
Traditional buttermilk is mainly consumed in India, Nepal and Pakistan.
Cultured buttermilk, commonly found in American supermarkets, generally does not have any probiotic benefits.
Buttermilk is low in fat and calories but contains several important vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin B12, riboflavin, calcium and phosphorus (17).
Bottom Line: Traditional buttermilk is a fermented dairy drink mainly consumed in India, Nepal and Pakistan. Cultured buttermilk, found in American supermarkets, does not have any probiotic benefits.
10. Natto

Natto is another fermented soybean product, like tempeh and miso.
It contains a bacterial strain called Bacillus subtilis.
Natto is a staple in Japanese kitchens. It is typically mixed with rice and served with breakfast.
It has a distinctive smell, slimy texture, and strong flavor. Natto is rich in protein and vitamin K2, which is important for bone health and cardiovascular health (17, 30, 31).
A study in older Japanese men found that consuming natto on a regular basis was associated with higher bone mineral density. This is attributed to the high vitamin K2 content of natto (32).
Other studies suggest that natto may help prevent osteoporosis in women (33, 34).
Bottom Line: Natto is a fermented soy product that is a staple in Japanese kitchens. It contains a high amount of vitamin K2, which may help prevent osteoporosis and heart attacks.
11. Some Types of Cheese

Therefore, it is important to look for live and active cultures on the food labels.
The good bacteria survive the aging process in some cheeses, including Gouda, mozzarella, cheddar and cottage cheese (35, 36).
Cheese is highly nutritious and is a very good source of protein. It is also rich in important vitamins and minerals, including calcium, vitamin B12, phosphorus and selenium (37).
Moderate consumption of dairy products, such as cheese, may even lower the risk of heart disease and osteoporosis (38, 39).
Bottom Line: Only some types of cheese contain probiotics, including cheddar, mozzarella, and gouda. Cheese is very nutritious, and may benefit heart and bone health.
Probiotic Foods Are Incredibly Healthy
There are many super healthy probiotic foods you can eat.
This includes numerous varieties of fermented soybeans, dairy, and vegetables. Eleven of those are mentioned here, but there are many more out there.
If you can�t or won�t eat any of these foods, then you can also take a probiotic supplement. There are many types available on Amazon.
Probiotics, from both foods and supplements, can have powerful effects on health.